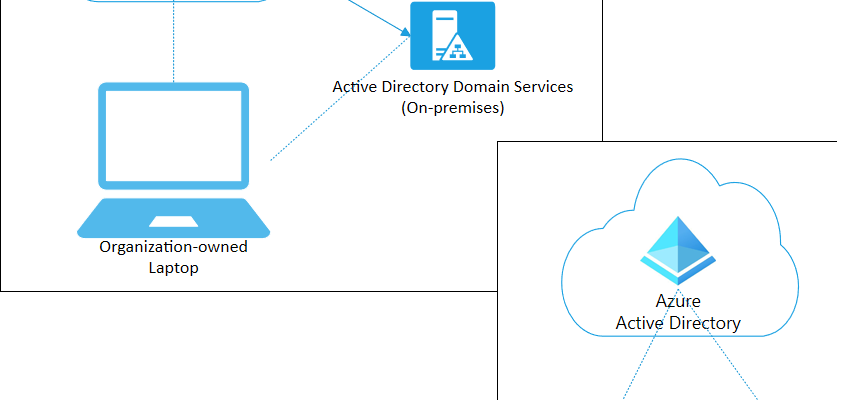
To protect the organisation’s assets, IT staff must first manage the device identities. IT staff can build on the device identity with tools like Microsoft Intune to ensure standards for security and compliance are met. Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) enables single sign-on to devices, apps, and services from anywhere through these devices. It’s a win-win situation for both!
- Users get access to your organization’s assets they need.
- IT staff / Security gets the controls they need to secure your organization.
Azure AD offers 3 Types of Device Registration / Joining mechanisms.
- Azure AD Registered devices
- Azure AD joined devices
- Hybrid Azure AD joined devices
The goal of Azure AD registered devices is to provide your users with support for the BYOD or mobile device scenarios. In these scenarios, a user can access your organization’s Azure Active Directory controlled resources using a personal device. Azure AD registered devices are signed in to using a local account like a Microsoft account on a Windows 10 device, but additionally have an Azure AD account attached for access to organizational resources.
| Azure AD registered | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Registered to Azure AD without requiring organizational account to sign in to the device |
| Primary audience | Applicable to Bring your own device (BYOD), and Mobile devices |
| Device ownership | User or Organization |
| Operating systems | Windows 10, Windows 11, iOS, Android, and macOS |
| Device sign in options | End-user local credentials, Password, Windows Hello, PIN Biometrics |
| Device management | Mobile Device Management (example: Microsoft Intune) |
| Key capabilities | SSO to cloud resources, Conditional Access |
Azure AD join is intended for organizations that want to be cloud-first or cloud-only. Azure AD join enables access to both cloud and on-premises apps and resources. Azure AD joined devices are signed in to using an organizational Azure AD account. Access to resources in the organization can be further limited based on that Azure AD account and Conditional Access policies applied to the device identity.
| Azure AD joined | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Joined only to Azure AD requiring organizational account to sign in to the device |
| Primary audience | Suitable for both cloud-only and hybrid organizations |
| Device ownership | Organization |
| Operating systems | All Windows 10 & 11 devices except Windows 10 Home |
| Device management | Mobile Device Management (example: Microsoft Intune) |
| Key capabilities | SSO to both cloud and on-premises resources, Conditional Access, Self-service Password Reset and Windows Hello PIN reset |
Organisations with an on-premises AD footprint can implement hybrid Azure AD joined devices. These devices are joined to your on-premises Active Directory and registered with your Azure Active Directory. This offers capability to use on-premise technology like GPO, Windows auth and win 7 support etc. Device writeback helps you to keep a track of devices registered with Azure AD in AD. You will have a copy of the device objects in the container “Registered Devices”. Also, Windows Hello For Business (WHFB) requires device writeback to in Hybrid- Federated scenarios.
| Hybrid Azure AD joined | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Joined to on-premises AD and Azure AD requiring organizational account to sign in to the device |
| Primary audience | Suitable for hybrid organizations with existing on-premises AD infrastructure |
| Device ownership | Organization |
| Operating systems | Windows 11, 10, 8.1 and 7, along with Windows Server 2008/R2, 2012/R2, 2016 and 2019 |
| Device sign in options | Password or Windows Hello for Business |
| Device management | Group Policy, Configuration Manager standalone or co-management with Microsoft Intune |
| Key capabilities | SSO to both cloud and on-premises resources, Conditional Access, Self-service Password Reset and Windows Hello PIN reset |